


- #1.5 volt battery chemistry manual#
- #1.5 volt battery chemistry upgrade#
- #1.5 volt battery chemistry portable#
When recharging, aluminum ions return to the anode, and it can exchange three redox electrons per cation. Aluminum-ionĪluminium-ion batteries are a class of rechargeable battery in which aluminum ions provide energy by flowing from the negative electrode of the battery, the cathode, to the positive electrode, the anode. However, an electric vehicle with aluminum batteries has the potential for up to eight times the range of a lithium-ion battery with a significantly lower total weight.
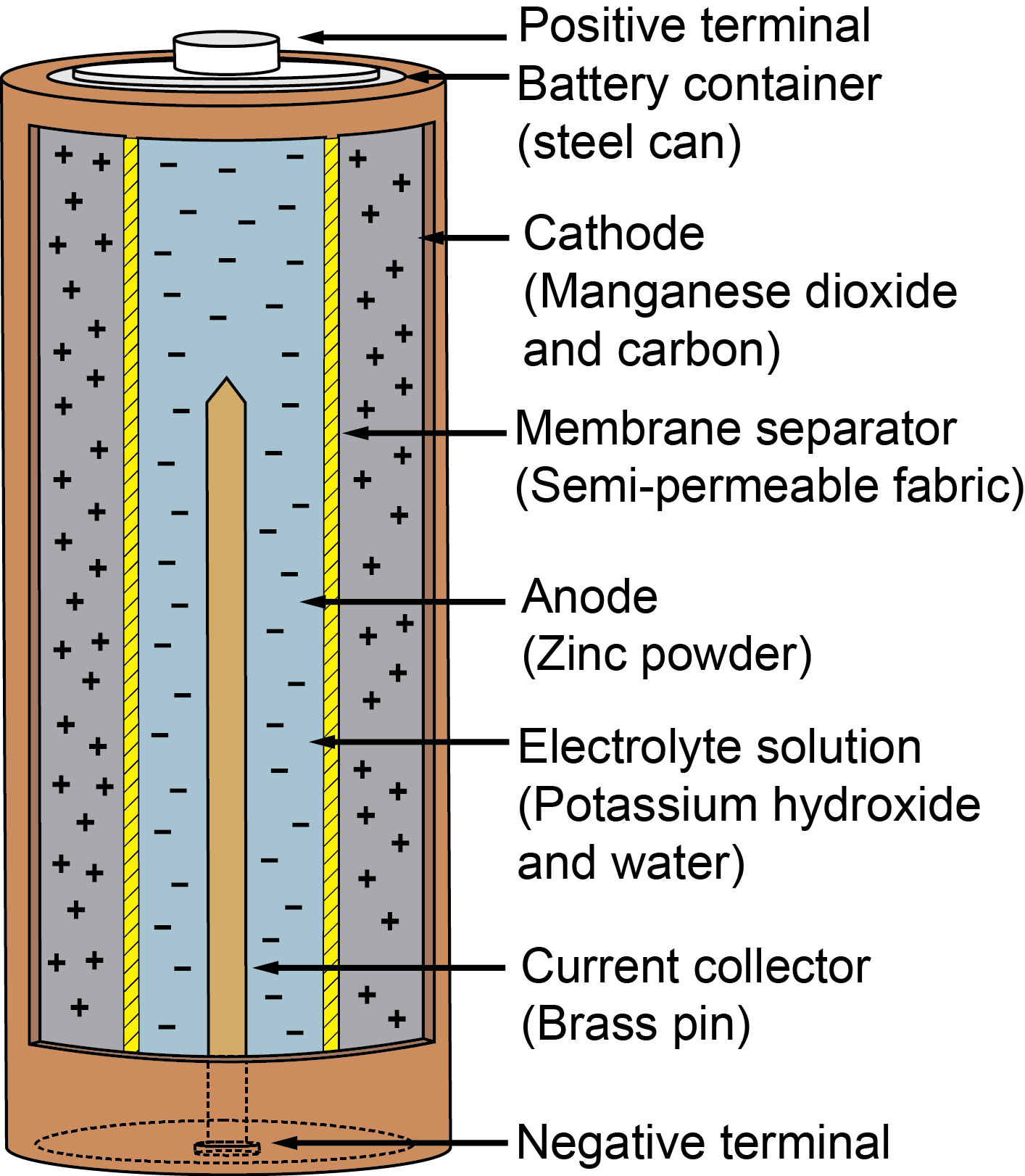
This has restricted their use to mainly military applications. They have one of the highest energy densities of all batteries, but they are not widely used because of problems with high anode cost and byproduct removal when using traditional electrolytes. AluminumĪluminium–air batteries produce electricity from the reaction of oxygen in the air with aluminum. This will ensure your battery remains healthy. Batteries can be discharged by unplugging the device's AC adapter and letting the device run on the battery until it ceases to function. The way to avoid the dreaded memory effect is to fully cycle (fully charge and then fully discharge) your battery at least once every two to three weeks. Your battery will remain functional, but only at 50% of its original capacity. To illustrate: If you, on a regular basis, fully charge your battery and then use only 50% of its capacity before the next recharge, eventually the battery will become unaware of its extra 50% capacity which has remained unused. What this means is that if a battery is continually only partially discharged before re-charging, the battery forgets that it has the capacity to further discharge all the way down. NiCd batteries, and to a lesser extent NiMH batteries, suffer from what's called the memory effect. It will automatically list all of the battery types supported by your machine.
#1.5 volt battery chemistry manual#
Refer to your owner's manual to find out which rechargeable battery types your particular device supports, or simply use our search engine to find your device.
#1.5 volt battery chemistry portable#
Therefore, the portable device's charger must be properly configured to handle a given type of rechargeable battery. The difference between them stems from the fact that each type requires a different charging pattern to be properly recharged. NiCd, NiMH, and Li-ion are all fundamentally different from one another and cannot be substituted unless the device has been pre-configured from the factory to accept more than one type of rechargeable battery.
#1.5 volt battery chemistry upgrade#
Is it Possible to Upgrade My Device's Battery to a Newer Chemistry? They are also better for the environment because they don't contain toxic materials such as Cadmium or Mercury. Another reason Li-Ion batteries have become so popular is that they do not suffer from the memory effect AT ALL. This is crucial in applications such as camcorders or notebook computers, where the battery makes up a significant portion of the device's weight. Li-Ion batteries produce the same energy as NiMH batteries but weigh approximately 35% less. Li-Ion has quickly become the emerging standard for portable power in consumer devices. NiMH batteries are also more environmentally friendly than their NiCd counterparts since they do not contain heavy metals (which present serious landfill problems). NiMH batteries are less prone to develop this dreaded affliction and thus require less maintenance and care. NiMH also offers another major advantage: NiCd batteries tend to suffer from what is called the memory effect. What this translates into is increased run-time from the battery with no additional bulk to weigh down your portable device. In other words, pound for pound, NiMH delivers approximately 100% more capacity than its NiCad counterpart. NiCd and NiMH: the main difference between the two is the fact that NiMH batteries (the newer of the two technologies) offer higher energy densities than NiCads. Each type of rechargeable battery technology has its own unique characteristics: What Is Battery C Rating What Are The Different Types of Rechargeable Battery Chemistries/Technologies?īatteries in portable consumer devices (laptops and notebooks, camcorders, cellular phones, etc.) are principally made using either Nickel Cadmium (NiCd), Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) or Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) technologies. Battery General Information: Battery Quick Tips |


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
